SEMANTIC AND ONTOLOGY MANAGEMENT
Understand the meaning of your data
An organizations capacity to draw insights from their data is often limited by data silos. Affirma leverages semantics to provide your common conceptional definitions of data and incorporates the widest scope of interpretation.
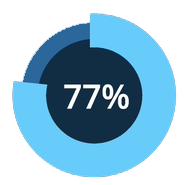
Organizations that take a semantic modeling approach are significantly more satisfied with analytics. [1]
 Affirma cited as a semantic-AI vendor in the Gartner Adopt a Data Semantics Approach to Drive Business Value report.
Affirma cited as a semantic-AI vendor in the Gartner Adopt a Data Semantics Approach to Drive Business Value report.
Ontology and semantic modeling
Represent your company’s data in a way that preserves its meaning and relationships within a specific context, independent of any technologies and vendor with a governed ontology. The ontology serves as an auditable enterprise business data model, easily understood by business stakeholders. It documents data lineage, consolidation, and harmonization rules from multiple sources. Import and leverage existing industry standards to accelerate critical areas such as natural language processing, data integration, knowledge representation, and artificial intelligence.
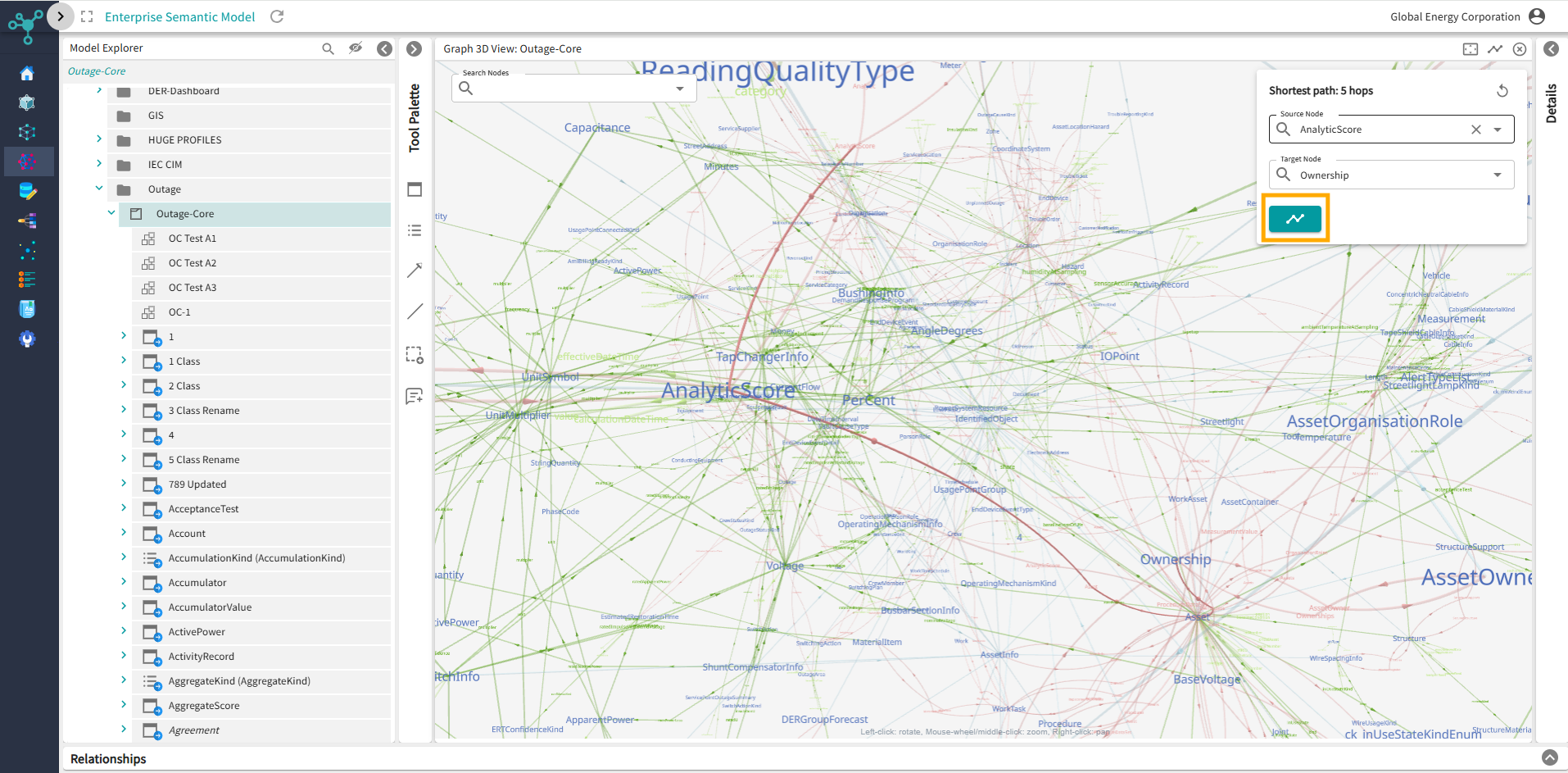
Knowledge Graph Viewer
The Knowledge Graph Viewer is made possible by Affirma’s intentional architecture, which adopts an ontology-based approach to represent metadata. It leverages W3C standards such as OWL, SKOS (Simple Knowledge Organization System), and ODRL (Open Digital Rights Language), among others.
- Deeper Insights
- Cross-Functional Clarity
- Complexity Made Intuitive
- Strategic Visibility
Mapping source data to semantics
Mapping data sources to a semantic model is essential for enabling interoperability, clarity, and usability of heterogeneous data within a unified framework. This process involves aligning the data structures from multiple sources with a defined semantic model or ontology, ensuring that all data conforms to a consistent structure that accurately reflects its meaning.
Common shared understanding of data
A centralized repository of data element definitions and descriptions acts as a reference guide for developers, data analysts, and other stakeholders. It offers clear insight into the structure, meaning, and usage of data across systems, enabling consistent understanding and effective use within the organization.

CEOs CONCERNED ABOUT INTEGRITY OF DATA
According to a KPMG report Trusted Analytics Mater to CEO'S, 56% of CEOs say they are concerned about the integrity of the data they are using for decision-making
Changing Your Data Management Reality
The reality we face today is an exponential growth of data with the potential to drive operational efficiencies and innovation. But this deluge of data needs to be managed, in a structured way, through processes, frameworks, practices and ideally driven by technology...
Garbage In Is Garbage out – The Importance of Data Labels
There is a common expression in technology domains being “garbage in, garbage out”. The expression was popular in the early days of computing and is even more relevant today as we utilize innovative technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence,...
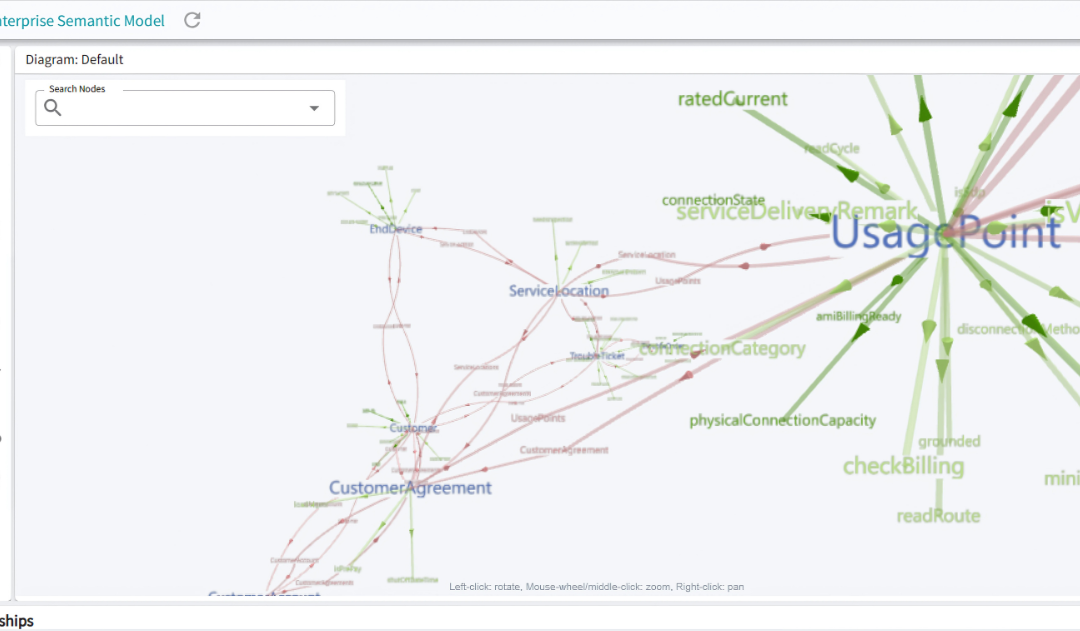
Affirma Product Update – Knowledge Graph Viewer
Visualization helps turn abstract ideas into tangible insights. Whether you are solving complex problems, aligning a team, or setting goals, being able to see something often makes it real and easier to grasp. To foster alignment and smarter decision-making, it's...